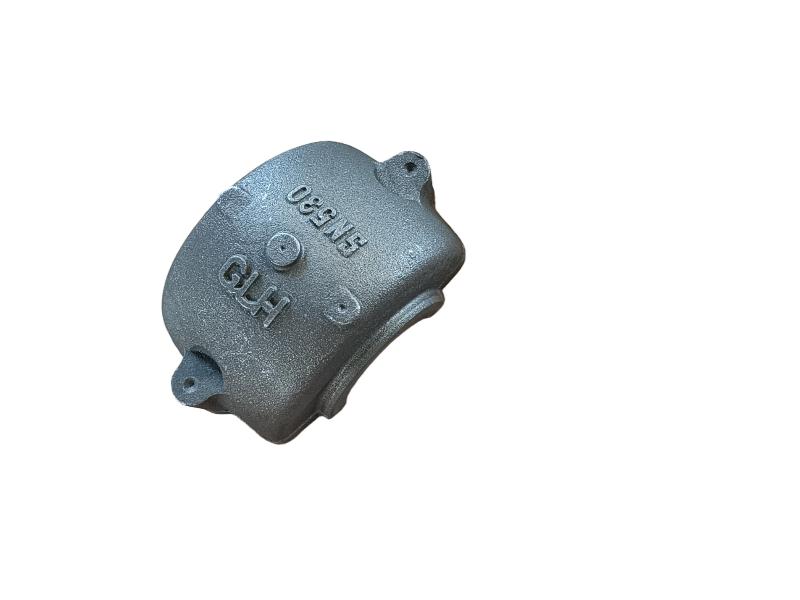
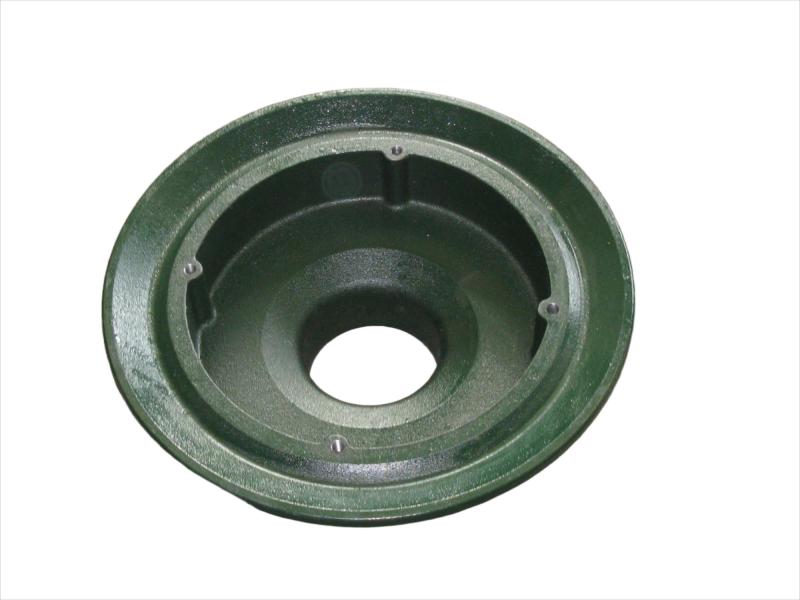
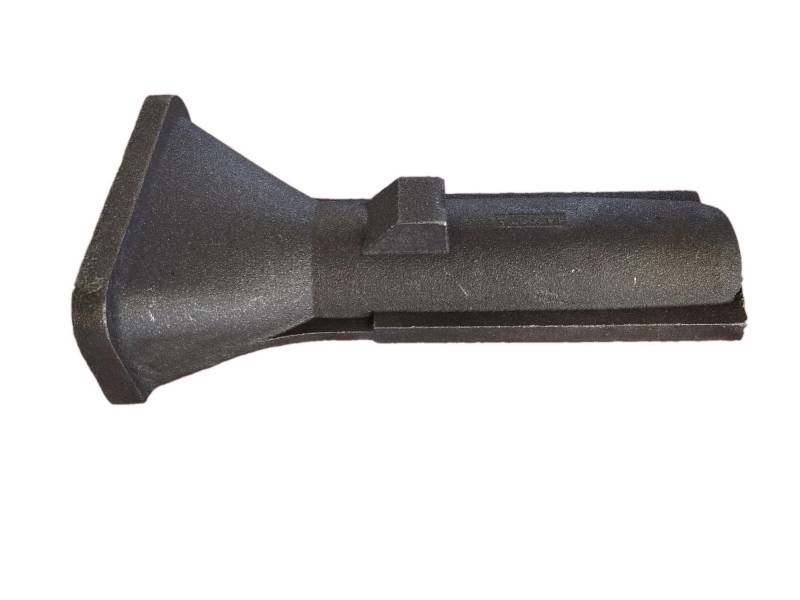
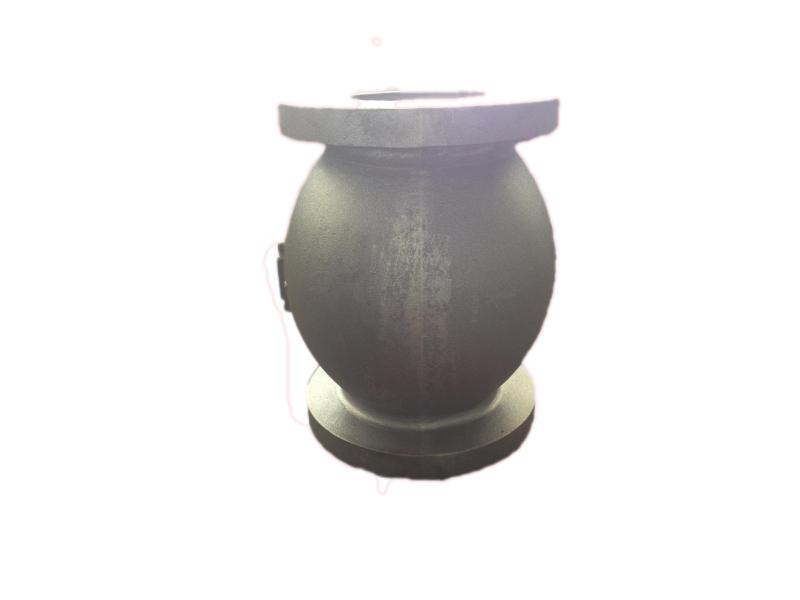
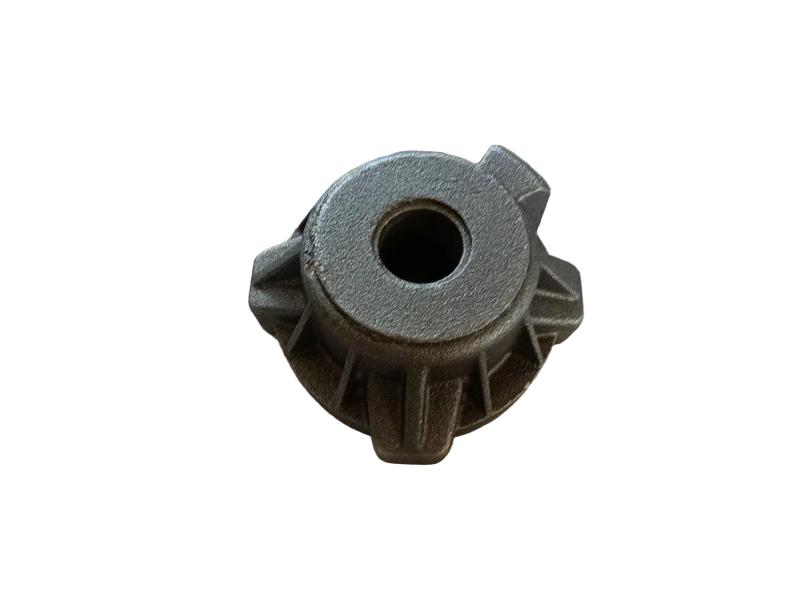
Valve disc is the initial valve trim component. The disc is the component that, depending on its position, enables, throttles, or stops the fluid flow. The name of the valve often originates from the type of disc. Examples include gate, ball, plug, and needle valves, which have discs that are the same shape as the name.
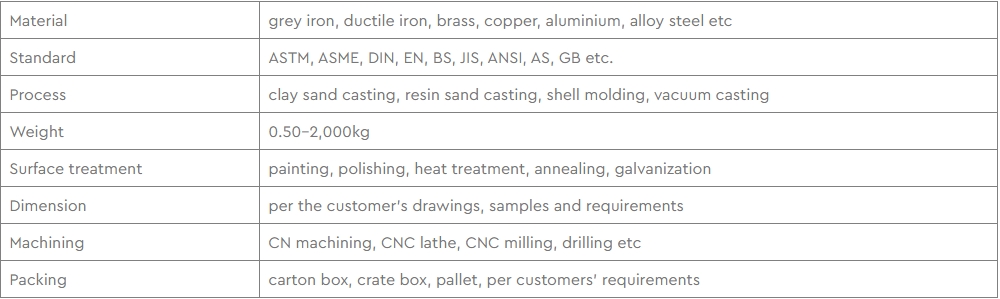
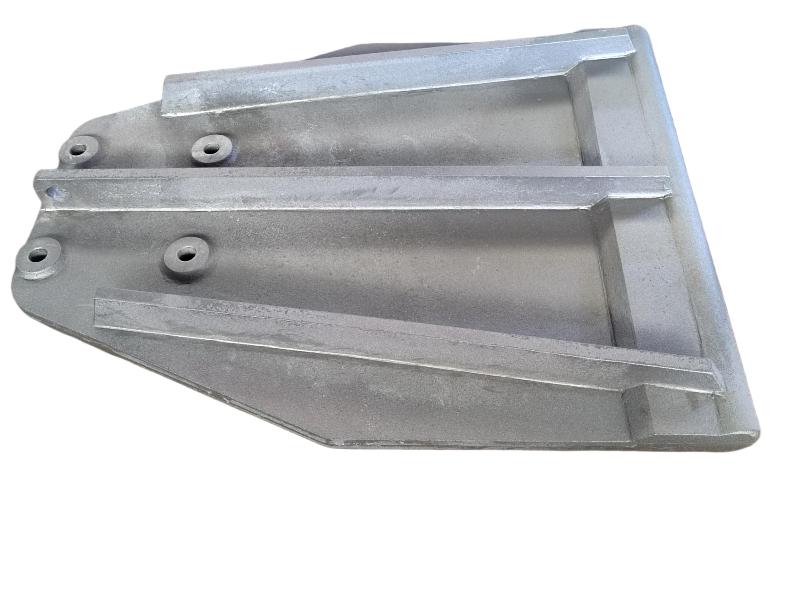
Hengchang is the leading producer of gray, ductile iron in China, melting more than 6000 tons per year, with more than 15 years experience. Customized butterfly valve disc are made of Ductile iron. Ductile iron, also known as ductile cast iron, nodular cast iron, spheroidal graphite iron, spheroidal graphite cast iron and SG iron, is a type of graphite-rich cast iron discovered in 1943 by Keith Millis .While most varieties of cast iron are weak in tension and brittle, ductile iron has much more impact and fatigue resistance, due to its nodular graphite inclusions.
Ductile iron is not a single material but part of a group of materials which can be produced with a wide range of properties through control of their microstructure. The common defining characteristic of this group of materials is the shape of the graphite. In ductile irons, graphite is in the form of nodules rather than flakes as in grey iron. Whereas sharp graphite flakes create stress concentration points within the metal matrix, rounded nodules inhibit the creation of cracks, thus providing the enhanced ductility that gives the alloy its name. Nodule formation is achieved by adding nodulizing elements, most commonly magnesium (magnesium boils at 1100 °C and iron melts at 1500 °C) and, less often now, cerium(usually in the form of mischmetal. Tellurium has also been used. Yttrium , often a component of mischmetal, has also been studied as a possible nodulizer.
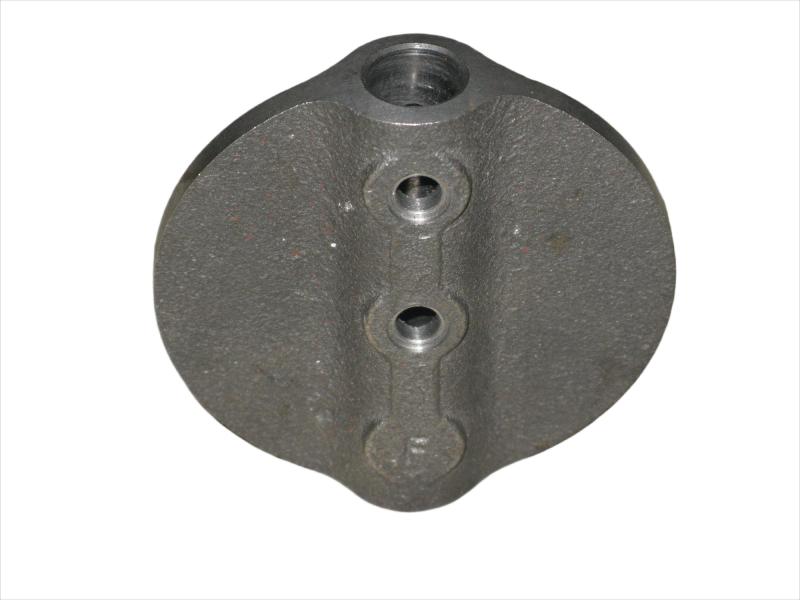
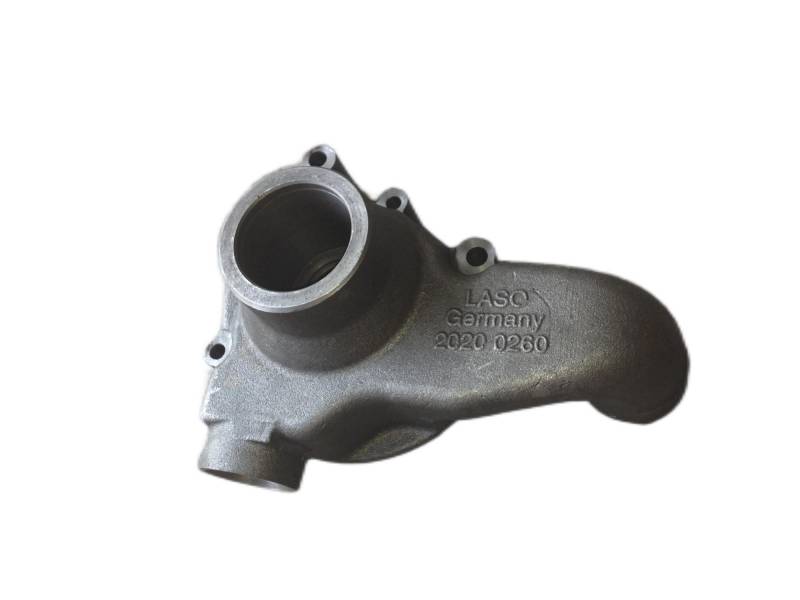
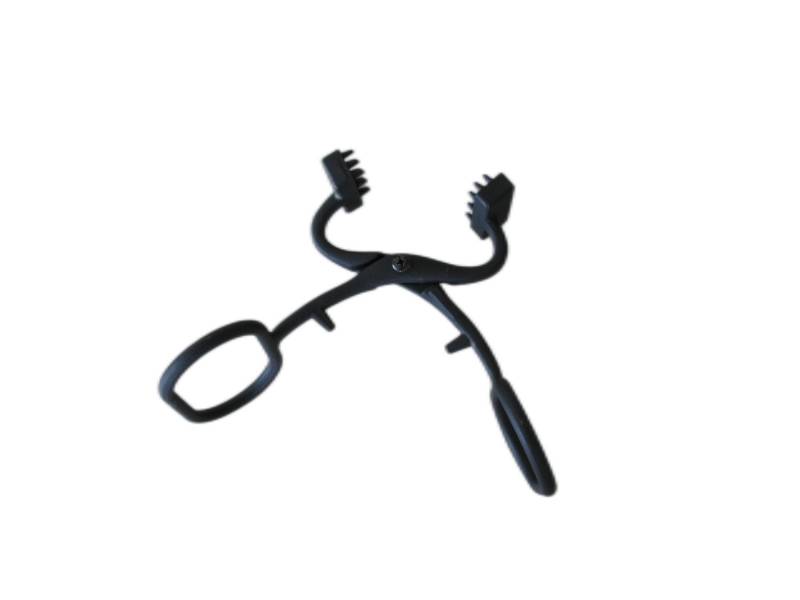
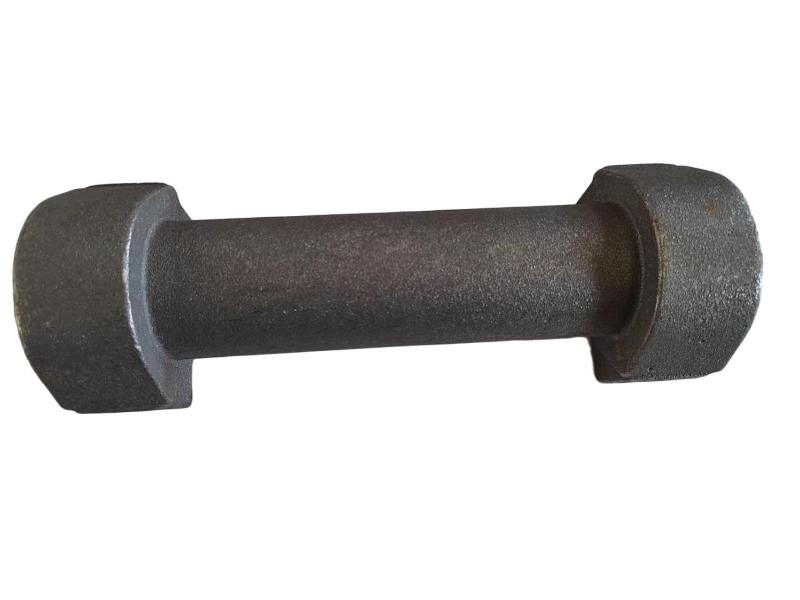
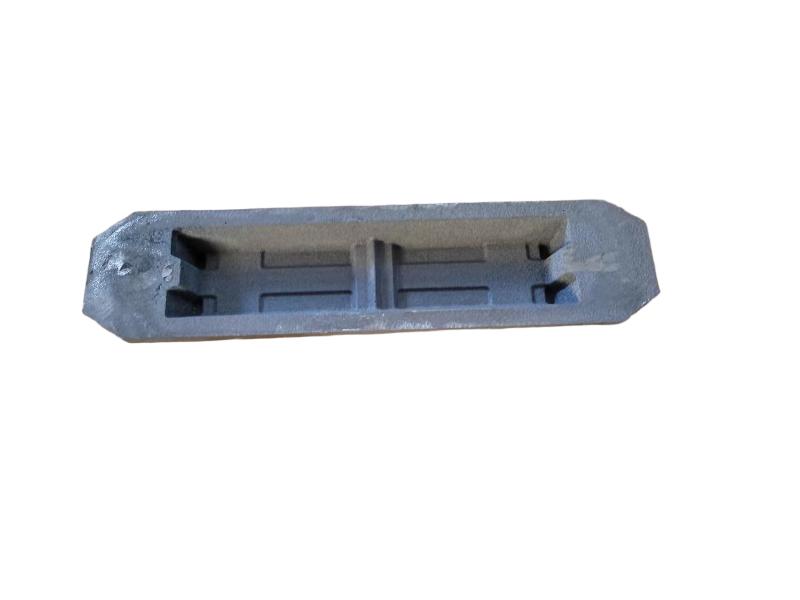
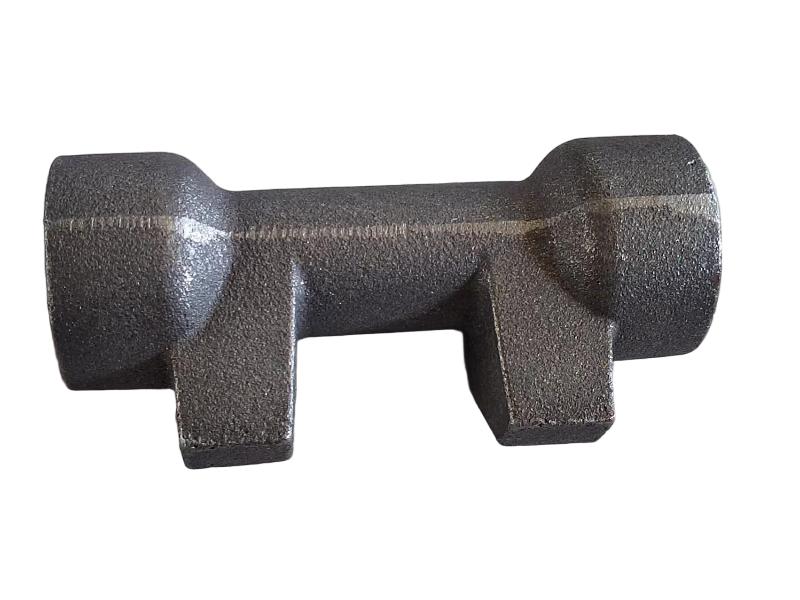
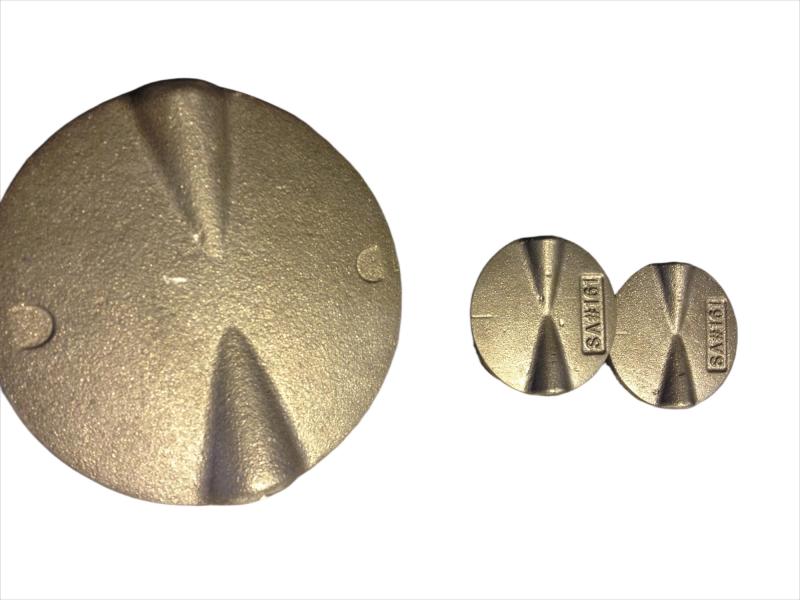
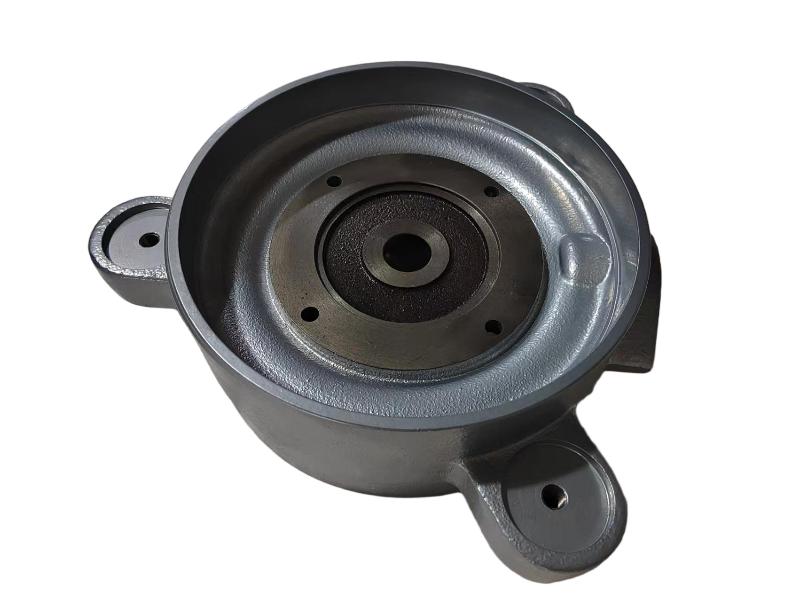
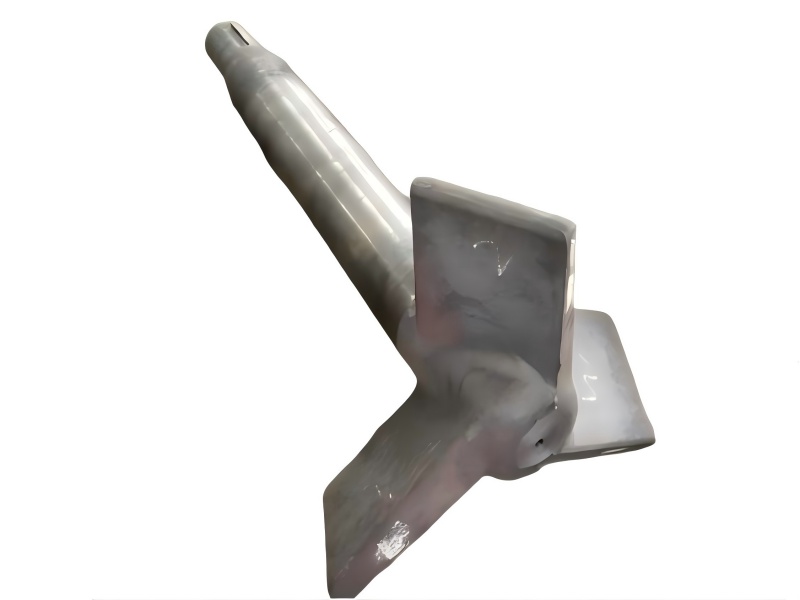
Some smaller iron casting parts include components as gears, pulleys, crankshafts, connecting rods, and propellers. Larger applications include housings for large equipment and heavy machine bases. Iron casting is also common in producing automobile components, such as engine blocks, engine manifolds, cylinder heads, transmission cases, and a full array of marine, agricultural, construction, industrial and Rail parts.
Machined casting products are used in several industries such as: Automotive, marine, agricultural, construction, industrial, earth moving, highway, and HVAC.
| Production Line Capabilities |
1.Vacuum Casting Line: Enables large-batch production and smooth surface medium parts

2.Resin Sand Casting Line: Delivers big complex geometries, but small quantity

3.Clay Sand Casting Line: Enables large-batch production small part and smooth surface medium parts

4.Medium-frequency Induction Furnace: Make sure uniform melting and stable quality

Comparative qualities of cast irons
| Name |
Nominal composition [% by weight] |
Form and condition |
Yield strength [ksi (0.2% offset)] |
Tensile strength [ksi] |
Elongation [%] |
Hardness [Brinell scale] |
Uses |
| Grey cast iron (ASTM A48) |
C 3.4, Si 1.8, Mn 0.5 |
Cast |
— |
50 |
0.5 |
260 |
Engine cylinder blocks, flywheels, gear box cases, machine-tool bases |
| White cast iron |
C 3.4, Si 0.7, Mn 0.6 |
Cast (as cast) |
— |
25 |
0 |
450 |
Bearing surfaces |
| Malleable iron (ASTM A47) |
C 2.5, Si 1.0, Mn 0.55 |
Cast (annealed) |
33 |
52 |
12 |
130 |
Axle bearings, track wheels, automotive crankshafts |
| Ductile or nodular iron |
C 3.4, P 0.1, Mn 0.4, Ni 1.0, Mg 0.06 |
Cast |
53 |
70 |
18 |
170 |
Gears, camshafts, crankshafts |
| Ductile or nodular iron (ASTM A339) |
— |
Cast (quench tempered) |
108 |
135 |
5 |
310 |
— |
| Ni-hard type 2 |
C 2.7, Si 0.6, Mn 0.5, Ni 4.5, Cr 2.0 |
Sand-cast |
— |
55 |
— |
550 |
High strength applications |
| Ni-resist type 2 |
C 3.0, Si 2.0, Mn 1.0, Ni 20.0, Cr 2.5 |
Cast |
— |
27 |
2 |
140 |
Resistance to heat and corrosion |






































 IPv6 网络支持
IPv6 网络支持
